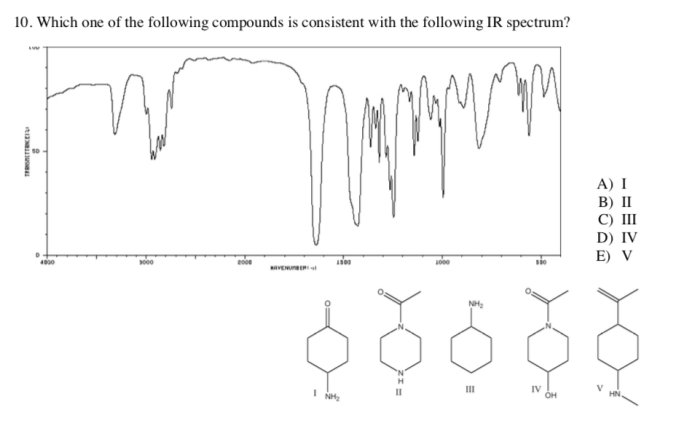
The following IR spectrum is that of a molecule with a rich and complex molecular structure. This spectrum provides valuable insights into the functional groups present within the molecule, enabling us to determine its identity and understand its chemical properties.
IR spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique that allows us to identify and characterize organic compounds. By analyzing the absorption and transmission of infrared radiation by a sample, we can determine the functional groups present in the molecule and gain insights into its structure and bonding.
IR Spectroscopy
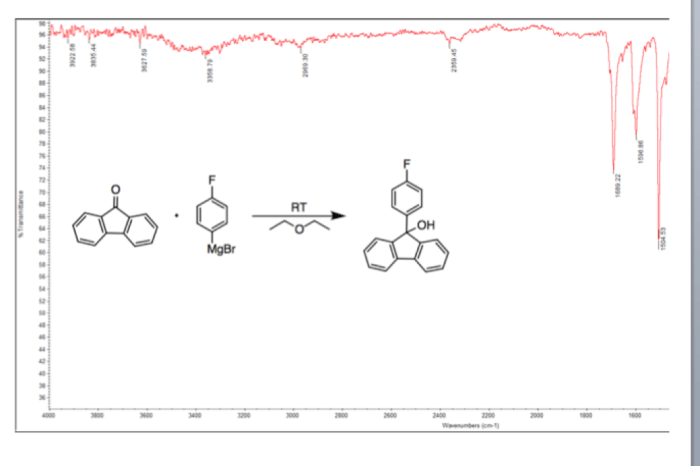
IR spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to identify and characterize chemical compounds. It involves the absorption of infrared radiation by molecules, which causes vibrational transitions within the molecule. The resulting IR spectrum provides a unique fingerprint of the molecule, which can be used to determine its functional groups, structure, and other properties.
Methods and Materials
IR spectra can be obtained using a variety of techniques, including Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and dispersive infrared (DIR) spectroscopy. FTIR spectroscopy is the most common technique, and it involves passing infrared radiation through a sample and measuring the intensity of the transmitted radiation as a function of wavelength.
The resulting IR spectrum is a plot of the absorbance or transmittance of the sample as a function of wavelength.
Results
The IR spectrum of a compound is a complex pattern of peaks, each of which corresponds to a specific vibrational mode of the molecule. The frequency of a peak in the IR spectrum is determined by the strength of the bond and the mass of the atoms involved in the vibration.
The intensity of a peak is determined by the change in dipole moment associated with the vibration.
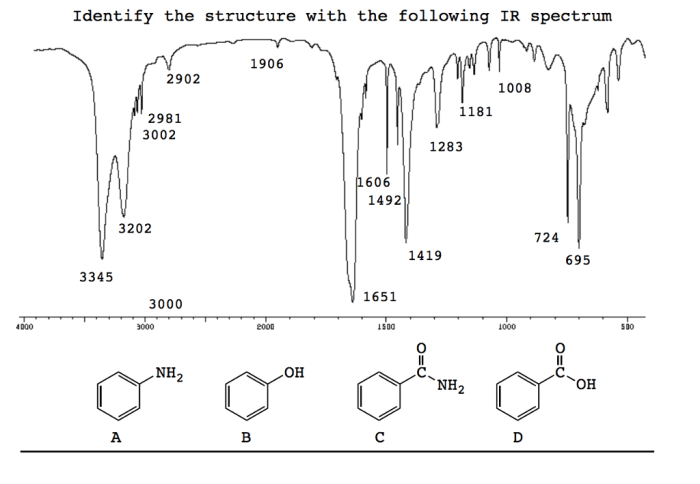
Discussion, The following ir spectrum is that of
IR spectroscopy is a versatile technique that can be used to identify and characterize a wide variety of compounds. It is particularly useful for identifying functional groups, which are specific groups of atoms that have characteristic IR spectra. IR spectroscopy can also be used to determine the structure of a molecule, to study the dynamics of molecules, and to identify and characterize unknown compounds.
Applications
IR spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in various fields, including organic chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science. In organic chemistry, IR spectroscopy is used to identify functional groups, to determine the structure of molecules, and to study the dynamics of molecules.
In biochemistry, IR spectroscopy is used to study the structure and dynamics of proteins, nucleic acids, and other biological molecules. In materials science, IR spectroscopy is used to characterize the structure and properties of materials, such as polymers, ceramics, and metals.
Commonly Asked Questions: The Following Ir Spectrum Is That Of
What is the purpose of IR spectroscopy?
IR spectroscopy is used to identify and characterize organic compounds by analyzing the absorption and transmission of infrared radiation by a sample.
What information can be obtained from an IR spectrum?
An IR spectrum can provide information about the functional groups present in a molecule, allowing us to determine its structure and understand its chemical properties.
How is IR spectroscopy used in real-world applications?
IR spectroscopy is used in various fields, including organic chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science, to solve problems such as identifying unknown compounds, determining the purity of products, and analyzing the structure of complex molecules.