Congenital heart defects nclex questions – Congenital heart defects are among the most common birth defects, affecting approximately 1 in 100 newborns. These defects can range from mild to severe, and they can have a significant impact on a child’s health and development. NCLEX questions on congenital heart defects are essential for nurses to be able to provide competent care to these patients.
This guide will provide an overview of congenital heart defects, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management. It will also discuss the role of the nurse in caring for patients with congenital heart defects.
Congenital Heart Defects Overview
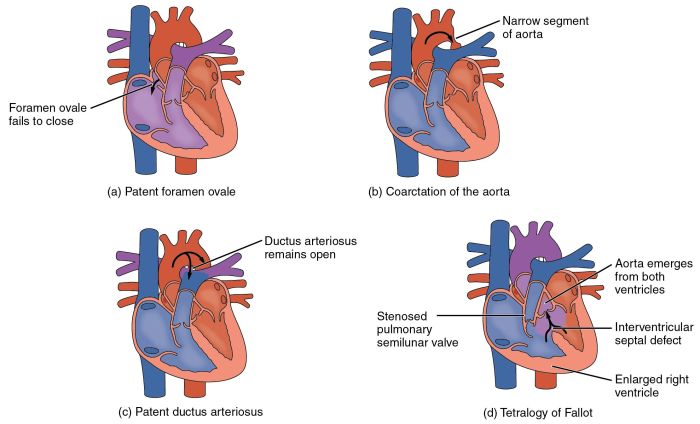
Congenital heart defects (CHDs) are structural abnormalities of the heart and blood vessels that are present at birth. They are the most common type of birth defect, affecting approximately 1% of live births. CHDs can range from mild to severe, and some may require lifelong treatment.The
causes of CHDs are not fully understood, but they are thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some risk factors for CHDs include:
- Maternal diabetes
- Maternal rubella infection
- Alcohol use during pregnancy
- Smoking during pregnancy
- Certain medications taken during pregnancy
There are many different types of CHDs, but the most common include:
- Atrial septal defect (ASD)
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Pulmonary stenosis
Assessment of Congenital Heart Defects: Congenital Heart Defects Nclex Questions

The signs and symptoms of CHDs can vary depending on the type of defect. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Cyanosis (bluish tint to the skin, lips, or nail beds)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Difficulty feeding
- Chest pain
- Heart murmurs
CHDs are diagnosed using a variety of methods, including:
- Physical examination
- Chest X-ray
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac catheterization
Early detection and diagnosis of CHDs is important because it allows for early treatment, which can improve the outcome.
Management of Congenital Heart Defects
The treatment of CHDs depends on the type and severity of the defect. Some CHDs can be treated with medication, while others require surgery.Medications that are used to treat CHDs include:
- Diuretics
- ACE inhibitors
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
Surgery is often necessary to repair or replace damaged heart valves or blood vessels. The type of surgery that is performed will depend on the specific CHD.
Nursing Care for Congenital Heart Defects
Nurses play an important role in the care of patients with CHDs. They provide education, support, and care to patients and their families.Nursing interventions for CHDs include:
- Monitoring vital signs
- Administering medications
- Providing wound care
- Teaching patients about their condition and treatment
- Supporting patients and their families emotionally
FAQ Insights
What are the most common types of congenital heart defects?
The most common types of congenital heart defects include septal defects, such as atrial septal defect (ASD) and ventricular septal defect (VSD), and conotruncal defects, such as tetralogy of Fallot and truncus arteriosus.
What are the signs and symptoms of congenital heart defects?
The signs and symptoms of congenital heart defects can vary depending on the type of defect. However, some common signs and symptoms include cyanosis (bluish skin), shortness of breath, fatigue, and difficulty feeding.
How are congenital heart defects diagnosed?
Congenital heart defects are diagnosed using a variety of tests, including echocardiography, electrocardiography, and cardiac catheterization.
How are congenital heart defects treated?
The treatment for congenital heart defects depends on the type and severity of the defect. Treatment options may include surgery, medication, or a combination of both.