Correctly label the following anatomical features of the oral cavity – Correctly labeling the anatomical features of the oral cavity is essential for understanding the structure and function of this vital region. From the buccal cavity to the palate and tongue, each component plays a crucial role in oral health and overall well-being.
This comprehensive guide will provide a detailed overview of the oral cavity’s anatomical features, empowering readers with the knowledge to accurately identify and understand their significance.
Buccal Cavity Features
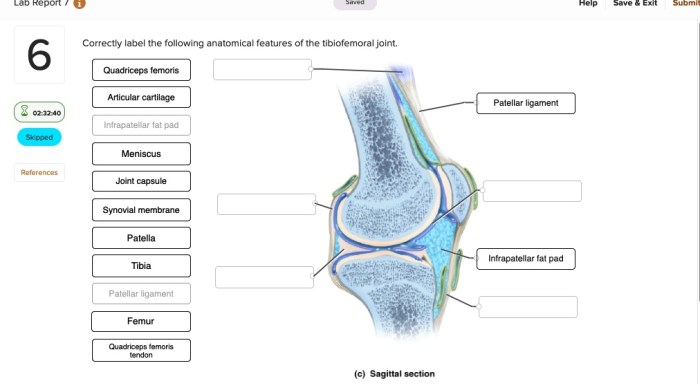
The buccal cavity, also known as the oral cavity, is the space within the mouth. It is lined by mucous membrane and contains the teeth, tongue, and other structures involved in speech, mastication, and swallowing.
| Anatomical Feature | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Papillae | Small, finger-like projections on the tongue and other surfaces of the oral cavity | Aid in taste sensation and mechanical stimulation |
| Frenulum | A fold of mucous membrane that connects the tongue to the floor of the mouth or the lips to the gums | Limits the movement of the tongue and lips |
| Gingiva | The gums, which surround the teeth and help to hold them in place | Protects the teeth and underlying bone |
| Vestibule | The space between the teeth and the cheeks or lips | Allows for the passage of food and saliva |
| Sulcus | The groove between the teeth and the gums | Traps food and bacteria, which can lead to tooth decay and gum disease |
Dental Features
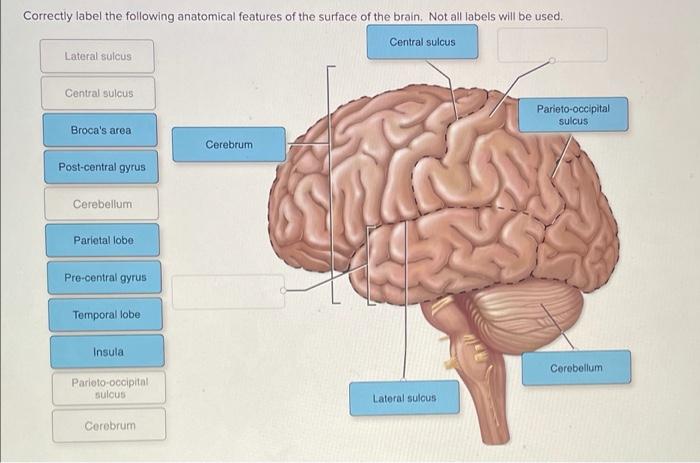
Teeth are hard, calcified structures that are embedded in the jaws. They are used for biting, chewing, and tearing food.
Structure of a Tooth, Correctly label the following anatomical features of the oral cavity
- Crown:The visible part of the tooth above the gum line
- Root:The part of the tooth that is embedded in the jawbone
- Pulp:The soft tissue in the center of the tooth that contains blood vessels and nerves
Types of Teeth
| Tooth Type | Number of Cusps | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Incisors | 1 | Cutting and biting food |
| Canines | 1 | Tearing and shredding food |
| Premolars | 2 | Grinding and crushing food |
| Molars | 3-5 | Grinding and crushing food |
Tongue Features: Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of The Oral Cavity
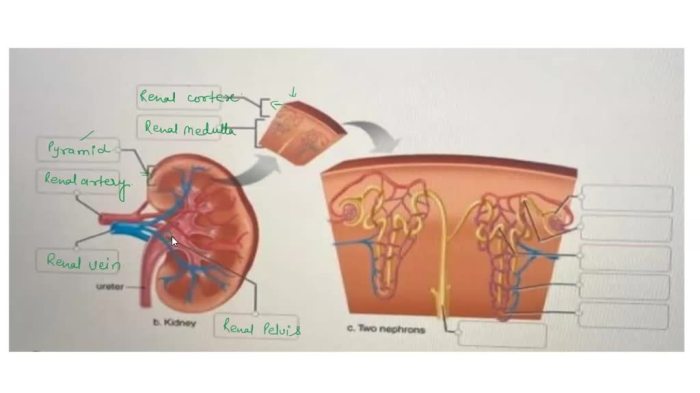
The tongue is a muscular organ that is located in the floor of the mouth. It is used for tasting, speaking, and swallowing.
Types of Papillae on the Tongue
- Filiform papillae: Small, pointed papillae that cover the majority of the tongue’s surface
- Fungiform papillae: Larger, mushroom-shaped papillae that are located on the tip and sides of the tongue
- Circumvallate papillae: Large, circular papillae that are located at the back of the tongue
- Foliate papillae: Leaf-shaped papillae that are located on the sides of the tongue
Palate Features
The palate is the roof of the mouth. It is divided into two parts: the hard palate and the soft palate.
Hard Palate
The hard palate is the anterior part of the palate that is formed by the maxilla and palatine bones. It is covered by mucous membrane and contains the incisive foramen, which is an opening that allows for the passage of nerves and blood vessels.
Soft Palate
The soft palate is the posterior part of the palate that is formed by the palatine aponeurosis and muscles. It is covered by mucous membrane and contains the uvula, which is a small, fleshy projection that hangs down from the center of the soft palate.
Floor of the Mouth Features
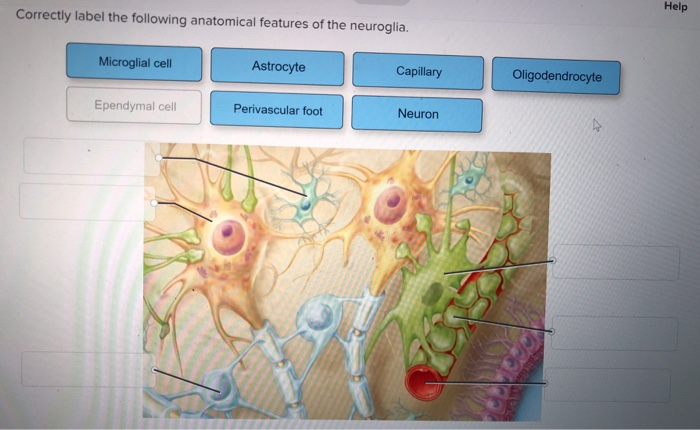
The floor of the mouth is the inferior part of the oral cavity. It is formed by the mylohyoid muscle, which is a thin, fan-shaped muscle that covers the floor of the mouth.
| Anatomical Feature | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Sublingual gland | Beneath the tongue | Produces saliva |
| Submandibular gland | Beneath the mandible | Produces saliva |
| Frenulum | A fold of mucous membrane that connects the tongue to the floor of the mouth | Limits the movement of the tongue |
| Mylohyoid muscle | Covers the floor of the mouth | Elevates the floor of the mouth during swallowing |
Salivary Glands
The salivary glands are glands that produce saliva, which is a clear, watery fluid that helps to moisten the mouth, lubricate food, and aid in digestion.
Location and Function of the Major Salivary Glands
- Parotid glands:Located on either side of the face, just below the ears. They produce serous saliva, which is thin and watery.
- Submandibular glands:Located beneath the mandible. They produce mixed saliva, which contains both serous and mucous components.
- Sublingual glands:Located beneath the tongue. They produce mucous saliva, which is thick and viscous.
FAQ Summary
What is the function of the buccal cavity?
The buccal cavity serves as the initial point of contact for food and liquids entering the digestive system. It also plays a role in speech production and facial expressions.
How many types of papillae are found on the tongue?
There are four main types of papillae on the tongue: filiform, fungiform, circumvallate, and foliate.
What is the difference between the hard palate and the soft palate?
The hard palate is the anterior portion of the palate and is formed by the maxilla and palatine bones. The soft palate is the posterior portion and is composed of muscle and connective tissue.