Modules 10 – 13: l2 security and wlans exam – Embarking on a comprehensive exploration of modules 10-13: L2 security and WLANs exam, this discourse delves into the intricacies of Layer 2 network security and wireless LANs, providing a profound understanding of threats, mitigation techniques, and best practices.
Unveiling the vulnerabilities inherent in Layer 2 networks, we elucidate diverse security threats and equip you with robust mitigation strategies. Furthermore, we delve into the fundamentals of WLANs, examining their components, topologies, and inherent security considerations.
1. Security Threats and Mitigation Techniques in Layer 2 Networks

Layer 2 networks are vulnerable to a variety of security threats, including:
-
-*MAC address spoofing
Attackers can forge MAC addresses to gain unauthorized access to the network.
-*ARP poisoning
Attackers can send fake ARP messages to redirect traffic to their own devices.
-*VLAN hopping
Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in VLAN configurations to gain access to unauthorized VLANs.
Mitigation Techniques
To mitigate these threats, several techniques can be used:
-
-*Port security
Restricting the number of MAC addresses that can be connected to a port.
-*ARP inspection
Validating ARP messages to prevent ARP poisoning.
-*VLAN trunk security
Controlling which VLANs can be trunked between switches.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDSs) play a crucial role in Layer 2 security:
-
-*Firewalls
Filtering traffic based on source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
-*IDSs
Detecting and alerting on suspicious network activity.
2. Wireless LAN (WLAN) Fundamentals and Security Considerations: Modules 10 – 13: L2 Security And Wlans Exam
WLAN Definition and Components, Modules 10 – 13: l2 security and wlans exam
A WLAN is a wireless network that uses radio waves to connect devices. Its components include:
-
-*Access point (AP)
Connects wireless devices to the wired network.
-*Wireless client
Device that connects to the AP.
-*WLAN controller
Manages multiple APs and provides centralized control.
WLAN Topologies and Security Implications
WLAN topologies include:
-
-*Infrastructure mode
APs connect wireless clients to the wired network.
-*Ad-hoc mode
Wireless clients connect directly to each other without an AP.
Ad-hoc mode is less secure than infrastructure mode, as it lacks centralized control and security mechanisms.
WLAN Security Challenges and Best Practices
WLANs face unique security challenges, such as:
-
-*Interception of wireless signals
Attackers can intercept data transmitted over the air.
-*Rogue APs
Unauthorized APs can be set up to collect sensitive data.
Best practices for WLAN security include:
-
-*Strong encryption
Using robust encryption algorithms, such as WPA2 or WPA3.
-*Authentication
Requiring users to authenticate before connecting to the WLAN.
-*Regular security audits
Periodically checking for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
3. WLAN Encryption and Authentication Mechanisms

Encryption Algorithms
WLAN encryption algorithms include:
-
-*WEP
Weak and easily cracked.
-*WPA
Improved security over WEP.
-*WPA2
More robust than WPA.
-*WPA3
The latest and most secure encryption standard.
Authentication Mechanisms
WLAN authentication mechanisms include:
-
-*Open system
No authentication required.
-*Shared key
A shared secret is used for authentication.
-*802.1X
A secure authentication protocol that uses RADIUS servers.
Comparative Analysis
| Encryption Algorithm | Authentication Mechanism | Security ||—|—|—|| WEP | Open system, Shared key | Weak || WPA | Shared key, 802.1X | Improved || WPA2 | 802.1X | Strong || WPA3 | 802.1X | Very strong |
4. WLAN Access Control and Management
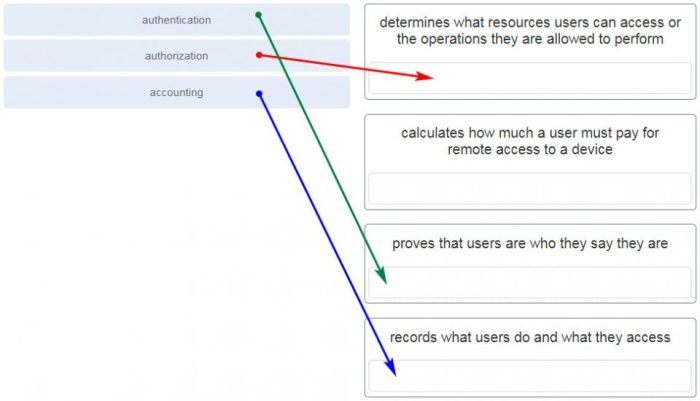
Access Control Methods
WLAN access control methods include:
-
-*MAC address filtering
Only allowing devices with specific MAC addresses to connect.
-*802.1X authentication
Requiring users to authenticate before connecting.
-*RADIUS servers
Centralized servers that store user credentials and grant access based on authentication.
WLAN Management Tools
WLAN management tools include:
-
-*WLAN controllers
Centralized management and control of multiple APs.
-*Network management systems (NMS)
Monitoring and managing WLANs from a single interface.
-*Wireless intrusion detection systems (WIDS)
Detecting and alerting on suspicious wireless activity.
Best Practices for Secure WLAN Management
-
-*Regular firmware updates
Updating AP firmware to patch vulnerabilities.
-*Secure configuration
Configuring APs securely and following best practices.
-*Monitoring and logging
Monitoring WLAN activity and logging security events.
5. WLAN Troubleshooting and Security Auditing
Common WLAN Problems
-
-*Connectivity issues
Devices unable to connect to the WLAN.
-*Slow performance
Poor network performance or dropped connections.
-*Security breaches
Unauthorized access or data breaches.
Troubleshooting Techniques
-
-*Checking connectivity
Verifying connectivity between devices and APs.
-*Analyzing performance
Monitoring network traffic and identifying performance bottlenecks.
-*Security audits
Regularly checking for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
WLAN Security Audit Steps
-
-*Planning
Defining the scope and objectives of the audit.
-*Scanning
Identifying all WLAN devices and vulnerabilities.
-*Assessment
Analyzing vulnerabilities and recommending remediation measures.
-*Reporting
Documenting the audit findings and recommendations.
FAQ Insights
What are the most common security threats to Layer 2 networks?
Layer 2 networks are susceptible to a range of threats, including ARP poisoning, MAC flooding, and VLAN hopping.
What are some effective mitigation techniques for WLAN security?
Implementing strong encryption algorithms, employing robust authentication mechanisms, and enforcing access control policies are crucial for WLAN security.
How can I troubleshoot common WLAN problems?
Troubleshooting WLAN problems involves identifying connectivity issues, signal strength optimization, and addressing interference.