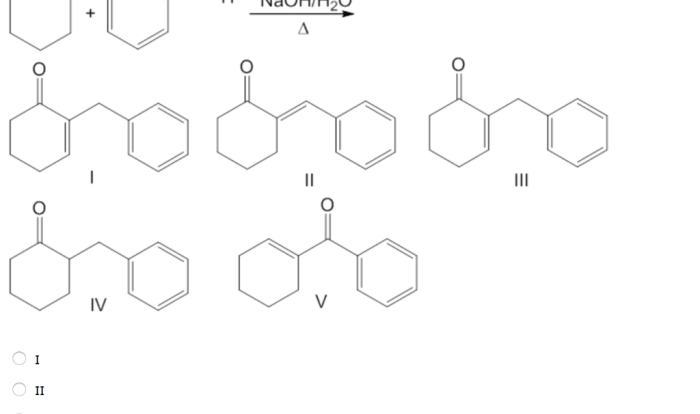
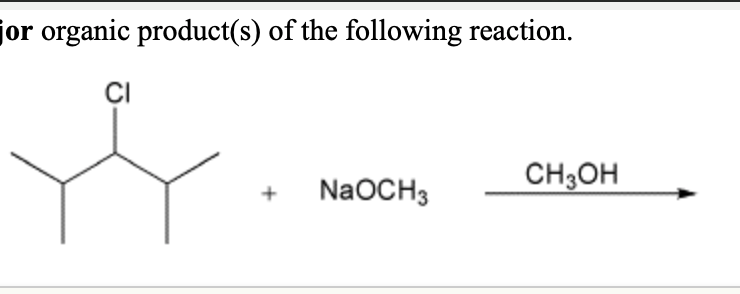
Draw the major organic product of the reaction conditions shown – Drawing the major organic product of reaction conditions is a crucial skill in organic chemistry, enabling chemists to predict the outcome of reactions and design synthetic strategies. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to drawing the major organic product, considering reaction conditions and various factors that influence product formation.
Understanding the major organic product is essential for comprehending reaction mechanisms, optimizing reaction yields, and developing new synthetic methods. By mastering this skill, chemists gain a deeper understanding of organic chemistry and its applications in various fields.
Introduction
In organic chemistry, the major organic product is the most abundant organic compound formed in a reaction. Understanding the major organic product is crucial for predicting the outcome of a reaction and designing synthetic strategies.
Reaction Conditions
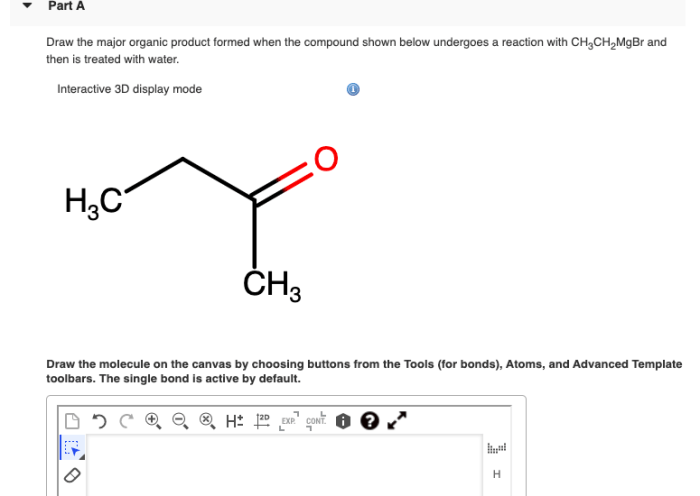
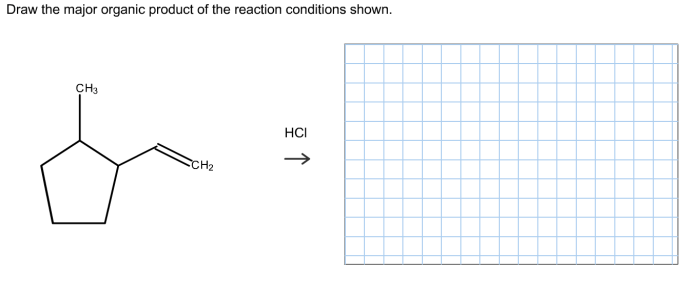
Reaction conditions play a significant role in determining the outcome of a reaction. Different reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, solvent, and catalyst, can influence the rate and selectivity of a reaction.
Types of Reaction Conditions
- Temperature: Temperature can affect the rate of a reaction, as well as the equilibrium position.
- Pressure: Pressure can affect the equilibrium position of a reaction, especially for gas-phase reactions.
- Solvent: The solvent can influence the solubility of the reactants and products, as well as the polarity of the reaction medium.
- Catalyst: A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed.
Drawing the Major Organic Product
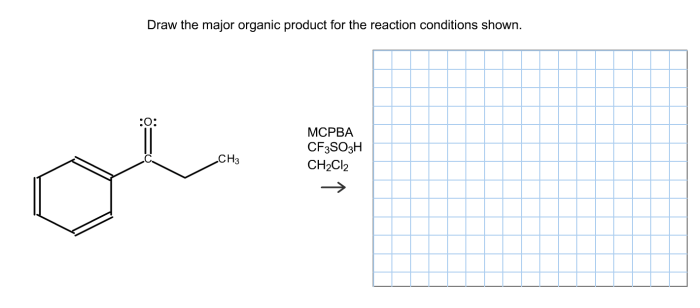
To draw the major organic product of a reaction, follow these steps:
- Identify the functional groups and bonds that are likely to be formed or broken in the reaction.
- Determine the most stable product based on factors such as electronegativity, resonance, and steric hindrance.
- Draw the structure of the major organic product using proper chemical notation.
Examples, Draw the major organic product of the reaction conditions shown
- In an addition reaction, the major organic product is typically the alkene with the most substituted double bond.
- In an elimination reaction, the major organic product is typically the alkene with the most stable double bond.
- In a substitution reaction, the major organic product is typically the compound with the most stable carbocation intermediate.
Factors Affecting the Major Organic Product
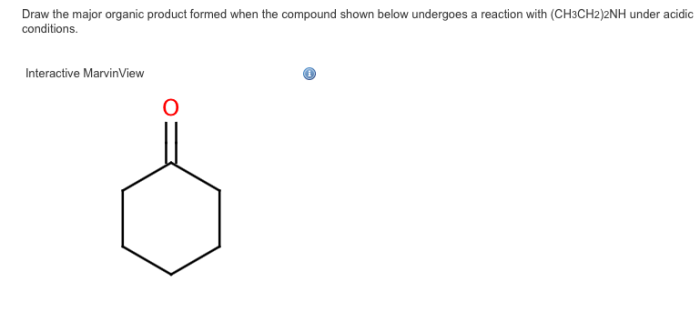
Several factors can affect the formation of the major organic product, including:
- Reaction mechanism: The mechanism of a reaction can influence the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of the reaction.
- Stereochemistry: The stereochemistry of the reactants can affect the formation of the major organic product.
- Kinetic vs. thermodynamic control: The conditions of the reaction can determine whether the major organic product is formed under kinetic or thermodynamic control.
Applications of Major Organic Product Analysis: Draw The Major Organic Product Of The Reaction Conditions Shown
The analysis of major organic products is used in various fields, including:
- Organic synthesis: Predicting the major organic product of a reaction is essential for designing synthetic strategies.
- Medicinal chemistry: Understanding the major organic product of a reaction is crucial for designing new drugs and therapies.
- Environmental chemistry: Analyzing the major organic products of environmental reactions helps in understanding the fate and transport of pollutants.
FAQ Resource
What are reaction conditions?
Reaction conditions refer to the specific parameters under which a chemical reaction takes place, such as temperature, pressure, solvent, and catalyst.
How do reaction conditions affect the major organic product?
Reaction conditions can significantly influence the major organic product by altering the reaction pathway and favoring certain product formations over others.
What factors can affect the formation of the major organic product?
Factors such as the stability of the products, steric effects, electronic effects, and solvent effects can influence the formation of the major organic product.